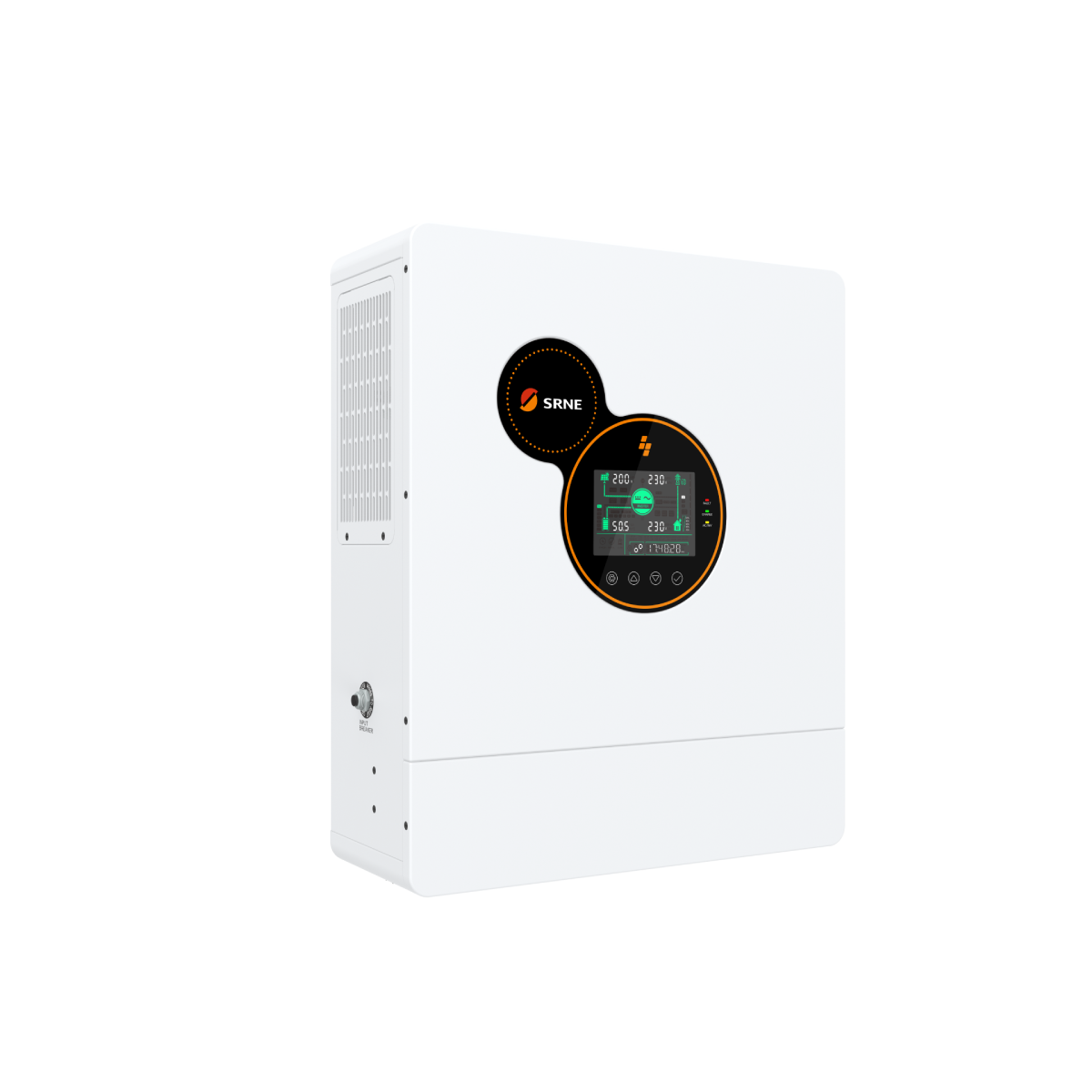
Hybrid Solar Inverters 101: How They Work & Why They’re Essential
In an era of rising energy costs and climate urgency, hybrid solar inverters are emerging as the cornerstone of
sustainable energy systems.
These devices bridge solar power, battery storage, and grid connectivity to deliver efficiency, reliability, and cost savings.
This guide unpacks hybrid solar inverter workings, real-world applications, and
why they’re transforming energy management globally.
1.What is a Hybrid Solar Inverter?
1.1A hybrid solar inverter is a versatile device that integrates three core functions:
Solar Conversion | Battery Storage | Grid Interaction |
Converts DC power from solar panels to AC electricity | Charges and discharges batteries to store excess energy. | Synchronizes with the utility grid for backup power or selling excess energy. |
1.2Key Components:
MPPT Controller | DC/AC Converter | Battery Management System (BMS) |
Maximizes energy harvest from panels. | Inverts solar/battery DC to usable AC. | ·Protects batteries from overcharge/discharge. |
1.3Technical Specification Example:
The Solis Hybrid Inverter (5kW model) achieves 98.5% efficiency, supports up to 150% DC oversizing,
and features a 10ms islanding response time.
2. How Hybrid Solar Inverters Work: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
2.1Phase 1: Solar Energy Harvesting
Process:
Solar panels generate DC power, which the hybrid inverter converts to AC for immediate use.
Excess energy charges the battery via the MPPT controller.
MPPT Optimization:The Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithm adjusts voltage/current to
extract peak energy from panels.
How MPPT Works:
Continuously monitors panel output.
Compares power output against a reference curve to find the optimal operating point.
Improves energy harvest by 15–30% compared to traditional PWM controllers.
Eg: A Sydney household using a Solis S5 Hybrid Inverter increased daily energy yield by 22% during winter months.
2.2Phase 2: Energy Distribution
The inverter prioritizes battery charging during low-demand periods (e.g., midday when solar production peaks).
Advanced algorithms optimize charging cycles to extend battery lifespan.
Dual-Mode Operation:
Mode | Function | Example |
Grid-Connected | Excess energy powers home loads or exports to the grid. | A Berlin apartment exports 12kWh/day to the grid, earning €0.15/kWh. |
Off-Grid | Battery powers critical loads during outages or peak pricing. | A Texas ranch uses a GoodWe ET10 to run pumps during grid outages. |
AC vs. DC Coupling:
concept | Pros | Cons | |
AC Coupling | Connects to existing grid-tie systems via AC input. | Lower installation cost, compatible with any solar panels. | Slightly lower efficiency (2–3% loss).
|
DC Coupling | Directly integrates with panels and batteries | Higher efficiency (98.5% vs 96.5%), faster response time.
| Requires compatible panels and batteries. |
2.3Phase 3: Battery Charging
The inverter prioritizes battery charging during low-demand periods (e.g., midday when solar production peaks).
Advanced algorithms optimize charging cycles to extend battery lifespan.
Smart Charging Strategies:
Time-of-Use (TOU) Charging | Surplus Solar Charging |
Charge batteries during low-rate periods (e.g., 2–6 AM).
| Automatically charges batteries when solar exceeds consumption. |
Battery Management:
Depth of Discharge (DoD):
Lithium-ion batteries | Lead-acid batteries |
80–90% DoD recommended.
| 50% DoD to extend lifespan. |
2.4Phase 4: Grid Backup & Islanding Mode
In the event of a grid outage, the inverter disconnects from the grid and powers critical loads using stored battery energy.
Grid Failure Response:
Islanding Detection:The inverter senses grid voltage/frequency instability.Response Time<20ms (critical for medical devices).
Load Prioritization:Powers essential loads first (e.g., refrigerators, medical equipment).
A Japanese hospital prioritizes ICU equipment during outages.
Case Study:
System: 5kW hybrid inverter + 12kWh battery (Panasonic HES5)
Outcome:Powered a 3-bedroom home for 18 hours during the 2024 Osaka blackout.
And prevented $600 in food spoilage and generator fuel costs.
2.5Phase 5: Grid Synchronization
The inverter ensures stable operation when connected to the grid, supporting voltage and frequency regulation.
Grid Support Features:
Voltage Regulation:Maintains grid voltage stability by injecting or absorbing reactive power.
Example: The SMA Sunny Boy Storage supports ±10% voltage regulation.
Frequency Control:Adjusts energy output to stabilize grid frequency (50/60Hz).
Critical for weak grids in developing countries.
3.Why Hybrid Solar Inverters Are a Game Changer?
3.1Cost Savings
Peak Shaving: Use stored energy during high-tariff hours.
A 2024 report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) found households using hybrid systems save 30–50% on electricity bills.
Net Metering: Sell excess energy to the grid in markets like California or Germany.
3.2Grid Independence
Islanding Mode: Continue operations during outages.
Case: A Texas hospital used a Huawei SUN2000-10KTL hybrid inverter to maintain critical services during Hurricane Idalia,
avoiding $200,000 in generator fuel costs.
3.3Environmental Impact
Reduce reliance on fossil fuels. A hybrid system paired with a 10kW solar array can offset
12 tons of CO₂ annually (equivalent to planting 600 trees).
3.4 Future-Proofing
V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) Ready: Charge electric vehicles and feed power back to the grid.
Scalability: Expand battery capacity as energy needs grow.
Hybrid Solar Inverter vs. Traditional Inverters
Feature | Hybrid Inverter | Grid-Tie Inverter | Off-Grid Inverter |
Grid Connection | Yes (bidirectional) | Yes (export only) | No |
Battery Support | Yes (AC/DC coupling) | No | Yes (DC coupling) |
Outage Protection | Yes (battery backup) | No | Yes |
Efficiency | 96–98% (with MPPT) | 95–97% | 94–96% |
Cost | $1,500–$3,000 (plus battery) | $500–$1,200 | $2,000–$4,000 (plus battery) |
4.Real-World Applications of Hybrid Solar Inverters
4.1Residential Energy Management
A Munich family installed a GoodWe ET10 with a 12kWh battery. Their solar self-consumption rose from 40% to 85%,
cutting annual energy costs by €1,800,reducing grid dependency and energy costs in a 4-person household.
And 4.5 tons CO₂ reduction annually (equivalent to 2,250 liters of gasoline saved).
4.2Commercial Use
A Bali resort used SRNE hybrid solar inverters with 50kWh batteries to reduce grid reliance by 60%,
saving $35,000 annually.Reduce diesel generator usage and energy costs in a 100-room resort.
4.3 Rural Electrification
Kenyan Project: Hybrid systems with Solis inverters provided 24/7 power to 50 villages,
enabling schools and clinics to operate reliably, And providing 24/7 electricity to 50 villages in off-grid regions.
Conclusion: Why Hybrid Solar Inverters Are a Must-Have
Hybrid solar inverters are no longer optional—they’re essential for maximizing energy independence,
reducing costs, and combating climate change. Whether you’re a homeowner, business owner,
or sustainability advocate, investing in a hybrid system is a smart move toward a greener, more resilient future.
Ready to upgrade your energy system? You can contact SRNE!Let's do it!