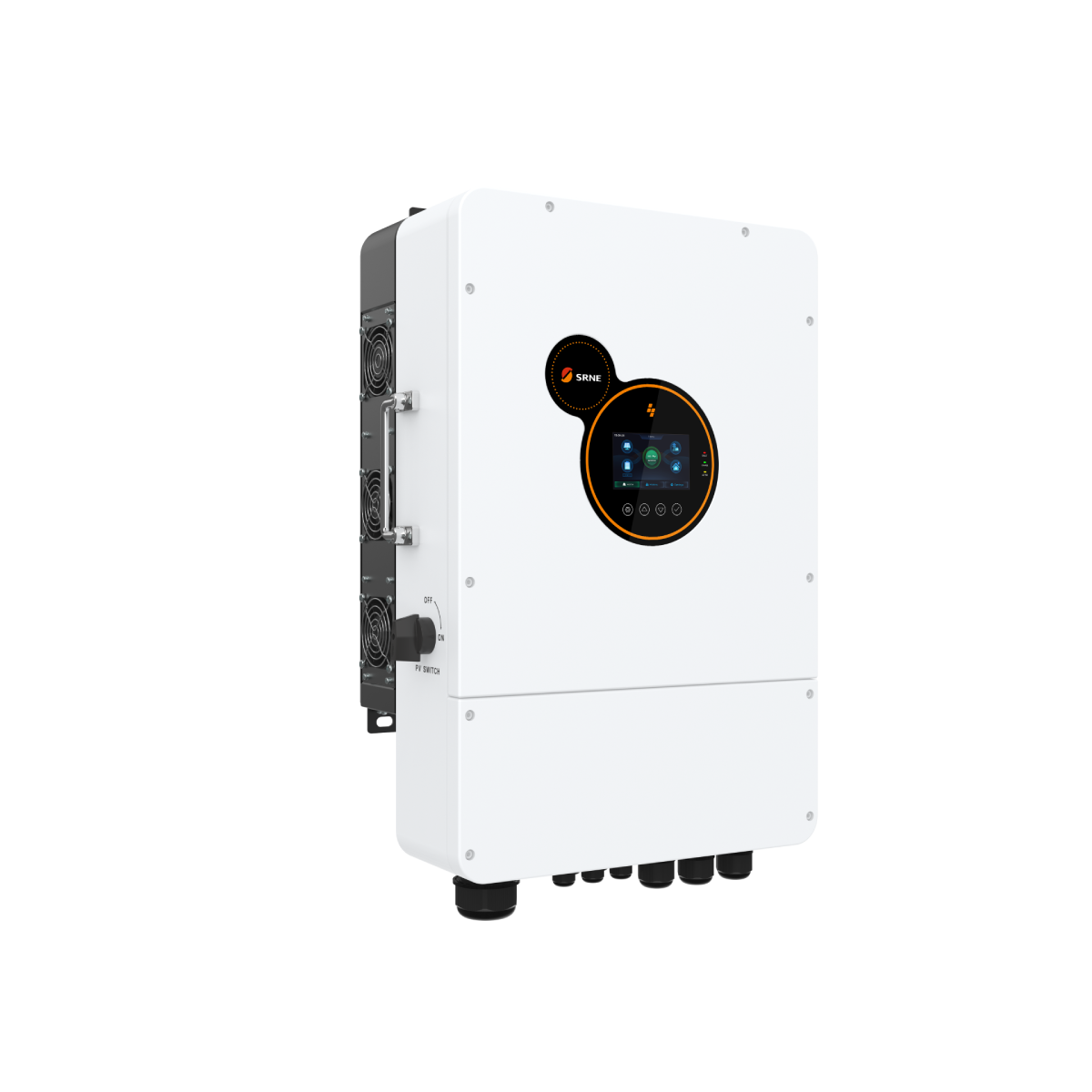
Home Energy Storage Inverters: Seamless Grid Switching
Introduction:
In an era where energy reliability and sustainability are paramount, homeowners are increasingly turning to
home energy storage systems to gain control over their power supply. At the heart of these systems lies a critical component:
the home storage inverter. But what sets the best inverters apart? The answer lies in seamless grid switching
—a technology that ensures uninterrupted power flow between grid-connected and off-grid modes,
protecting your home from outages while maximizing energy efficiency.
1.How Home EnergyStorage Inverters Ensure Seamless Grid Transition?
For homeowners seeking reliable power solutions, understanding how home storage inverter achieve
seamless off-grid to grid-tied switching is crucial. This technology ensures uninterrupted power supply,
optimizes energy usage, and enhances resilience against outages. Let’s explore the core mechanisms.
1.1 Storage Inverter Key Technical Modules
Grid Synchronization & Detection
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) | Dynamic Threshold Monitoring |
Uses advanced algorithms to track grid voltage phase, frequency, and amplitude with microsecond precision, ensuring perfect alignment between the inverter and grid. | Triggers switching when grid parameters exceed safe ranges (e.g., ±10% voltage deviation, ±0.5Hz frequency drift). |
Switching Strategy Design
Pre-Synchronization | Dual-Mode Operation |
Adjusts inverter output to match grid voltage (phase difference<3°, frequency difference <0.05Hz) before switching. | Grid-Tied Mode: Functions as a current source (PQ control) to follow grid current commands. Off-Grid Mode: Switches to voltage source (V/f control) to stabilize local power supply. |
Hardware Redundancy & Fast Switching
Thyristor + Relay Hybrid System | Bus Capacitor Energy Storage |
Combines thyristors (μs-level fast shutoff) for instantaneous switching and relays for long-term reliability. | Maintains power continuity during transitions with ≥10mF/1000V capacitors, ensuring minimal voltage drops. |
1.2Control Algorithms & System Coordination
Smart Switching Logic
Multi-Criteria Decision Making | Load Prioritization |
Integrates grid stability, battery state of charge (SOC), and load priorities to determine optimal switching timing. | Protects critical devices (e.g., medical equipment, Wi-Fi routers) during outages. |
Energy Management System (EMS) Integratio
Cloud-Based Monitoring | Virtual Synchronous Generator (VSG) |
Leverages IoT data to optimize switching strategies in real time. | Mimics traditional generator behavior to stabilize microgrids and improve grid resilience. |
2.Seamless Switching in Action
The core of seamless switching for energy storage inverters lies in the closed - loop design of
"pre - synchronization - rapid switching - stable control". By combining hardware redundancy and intelligent algorithms,
it ultimately achieves dual - mode switching that is imperceptible to users and causes no damage to equipment.
2.1 Synchronous control technology
Before switching, the output of the energy storage inverter is made to be completely synchronized with the phase, frequency,
and amplitude of the grid voltage to avoid switching shocks. This is mainly achieved through two technologies.
The Phase - Locked Loop (PLL) tracks the phase and frequency of the grid voltage in real - time to ensure that the output of
the energy storage inverter matches it. The other is the adaptive compensation algorithm, which dynamically adjusts
the output voltage to compensate for the effects of line impedance and load changes.
2.2 Rapid switching strategy
The switching time of the energy storage inverter is compressed to the millisecond level (usually < 20ms) to avoid load power outages.
Pre - synchronization technology
Before switching, the inverter output is made to be completely synchronized with the target power source (grid or energy storage),
eliminating phase differences, frequency differences, and voltage differences. This technology can be achieved through
phase synchronization, frequency synchronization, and voltage pre - adjustment.
Dual - mode parallel operation
First, we need to understand the grid - connected mode and the off - grid mode. The grid - connected mode is
current - source control (PQ control), which tracks the grid current command. The off - grid mode is
voltage - source control (V/f control), which maintains the stability of the local voltage.
At the moment of switching, the inverter is connected to both the grid and the energy storage, and
the main power supply is seamlessly switched through a fast switch (such as a thyristor or a solid - state relay).
Hardware redundancy design
A dual - DSP or FPGA architecture is adopted to accelerate the processing of control signals and reduce delays.
2.3 Voltage and frequency stable control
Droop control
In the off - grid mode, by adjusting the output voltage and frequency, the characteristics of the grid are simulated
to stabilize the micro - grid.
Active frequency deviation (AFD)
When connected to the grid, the grid frequency is monitored in real - time to quickly respond to grid fluctuations.
For example, during the off - grid switching, the storage inverter limits the voltage fluctuation to ±2% and
the frequency deviation to < 0.1Hz through droop control.
2.4 Fault detection and fault - tolerance mechanism
Storage inverter may be used in various places in the home, so safety is of great importance. Parameters such as
grid voltage, current, and temperature can be monitored through sensors to identify abnormalities
(such as grid power outages and short - circuits). If a grid fault is detected, the grid - connected contactor is
disconnected within 5ms, and the system switches to the off - grid mode to ensure electrical safety.
3. Operation process and user experience
3.1 Core logic of the operation process
The conditions for triggering the automatic switching process (automatically detected by the energy storage inverter) are as follows:
the grid voltage fluctuation exceeds the threshold (such as ±15% of the nominal voltage), the frequency deviation is
> ±0.5Hz (such as from 50Hz to 49.5Hz), the grid is interrupted (such as a blown fuse or a line fault), and the state of
charge (SOC) of the energy storage battery is lower than the preset value (such as 20%), which triggers protection.
3.2 User experience optimization design
This can be achieved through seamless switching and an intelligent interactive interface.
Seamless switching
This is achieved under certain key indicators, such as a switching time of < 20ms (industry standard) and
a voltage fluctuation of < ±3% (such as from 220V to 215V). When the German SMA Sunny Tripower switches,
the LED lights do not flicker, and the Wi - Fi interruption time is < 1ms.
Intelligent interactive interface
It has real - time status display, which can dynamically show the grid voltage, battery SOC, and load power.
It also uses colors to distinguish modes (green = grid - connected, orange = off - grid). When the energy storage inverter encounters
an abnormal situation, there are low - temperature/high - temperature alarms for the battery (such as < 0°C or > 50°C).
Conclusion:
Seamless grid switching in storage inverter isn’t just a technical feature—it’s a game-changer for modern living.
By combining lightning-fast transitions, intelligent energy management, and user-friendly design,
these systems offer peace of mind, cost savings, and a step toward a greener future.
In fact, the energy storage inverter is not only reflected in the home, but also in the RV, solar energy, etc.
If you need to understand other aspects, and even cost-effective, you can contact SRNE!