Hybrid Inverter And An Off-grid Inverter,Which One Is Better?
Among the popular options, hybrid inverters and off-grid inverters are often compared. But when it comes to building a dependable, truly independent energy system—especially in locations without stable grid access—off-grid inverters often hold a clear advantage. This article breaks down how both systems work, compares their key differences, and highlights real-world cases where off-grid inverters deliver unmatched performance.
Learn more:
https://www.srnesolar.com/articledetail/off-grid-inverters-the-best-choice-for-remote-areas.html
1.Understanding Hybrid and Off-Grid Inverters: How They work?
In any solar energy system, the solar inverter plays a central role by converting direct current (DC) from photovoltaic panels into alternating current (AC) used by most appliances. Among the available inverter technologies, hybrid inverters and off-grid inverters are two popular choices—each tailored to different usage environments and energy needs.
Hybrid inverters are designed to work across multiple energy inputs. They can coordinate power from solar arrays, batteries, and the electrical grid, switching between sources automatically depending on system demands and supply conditions. One of their notable advantages is the ability to export surplus solar power back to the grid, often under net metering policies. However, most hybrid models depend on a stable grid signal to operate efficiently, which can pose limitations in areas without consistent utility access. Additionally, the added complexity of managing multiple inputs often leads to higher costs and more involved installation procedures.
Learn more:
https://www.srnesolar.com/articledetail/the-ultimate-guide-to-solar-hybrid-inverters.html
On the other hand, off-grid inverters are purpose-built for independence from utility infrastructure. These systems draw energy solely from solar panels and battery banks to deliver electricity to local loads. Designed to function autonomously, they provide dependable power in areas without grid connectivity—making them ideal for rural homes, off-grid cabins, agricultural operations, mobile applications like RVs, or remote industrial setups. Though they lack the ability to interface with the grid, off-grid inverters typically offer a simpler, more rugged solution for standalone solar systems.
Learn more:
https://www.srnesolar.com/articledetail/off-grid-inverters-what-is-it-and-how-to-choose.html
In essence,MPPT hybrid inverters are well-suited for installations that benefit from both solar and grid resources, particularly in areas with partial or backup grid availability. Meanwhile, off-grid inverters excel in isolated environments where full self-reliance and reliability are critical.
2. Quick Comparison: Off Grid vs Hybrid Solar Inverters
Feature | Hybrid Inverter | Off-Grid Inverter |
Grid Connection | Optional (supports grid) | Not supported |
Battery Support | Yes | Yes |
Solar Integration | Yes | Yes |
Off-grid Capability | Limited or Conditional | Full, native support |
Complexity | Higher (needs config) | Lower, plug-and-play |
Cost | Typically higher | Generally more affordable |
Best for | Urban homes with backup | Remote locations, cabins |
3.Why Off-Grid Inverters Are Ideal for True Energy Independence
In locations where the utility grid is unavailable or unreliable, maintaining power continuity and self-sufficiency is critical. This is precisely where off-grid solar inverters excel. Unlike MPPT hybrid inverters—which often depend on a stable grid signal for synchronization—off-grid models are purpose-built to operate autonomously, without needing any utility reference. In fact, in the absence of grid input, many hybrid inverters can malfunction or switch to protection mode, making them unsuitable for fully isolated energy systems.
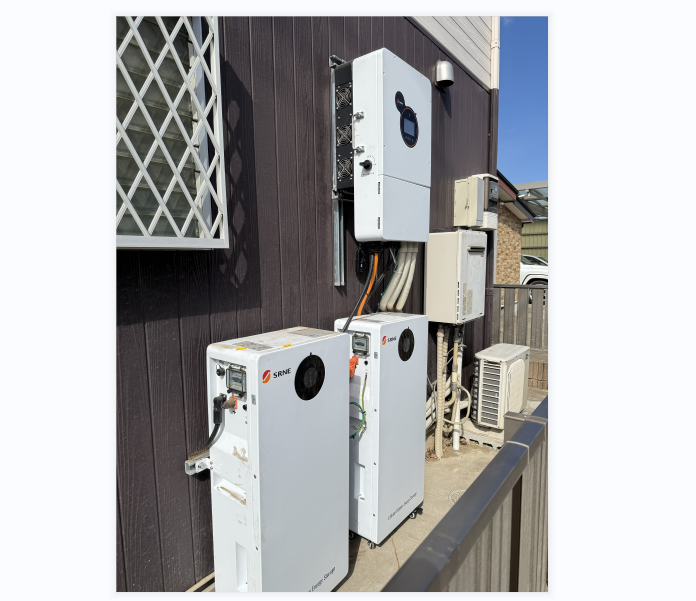
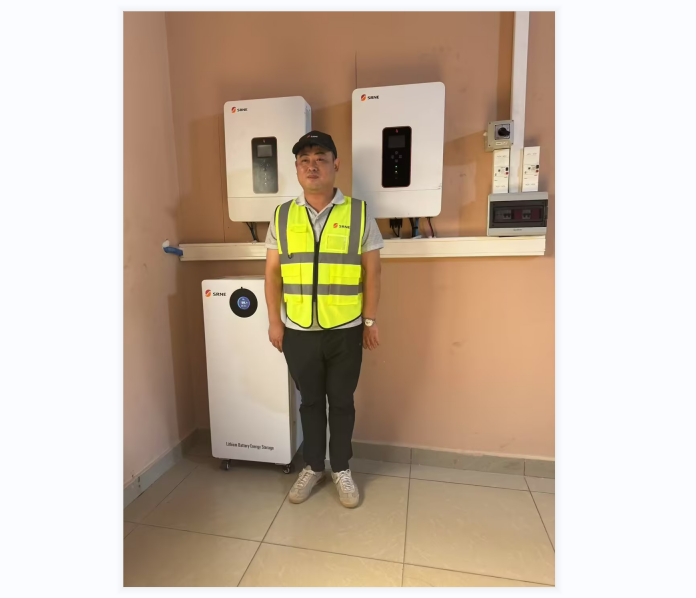
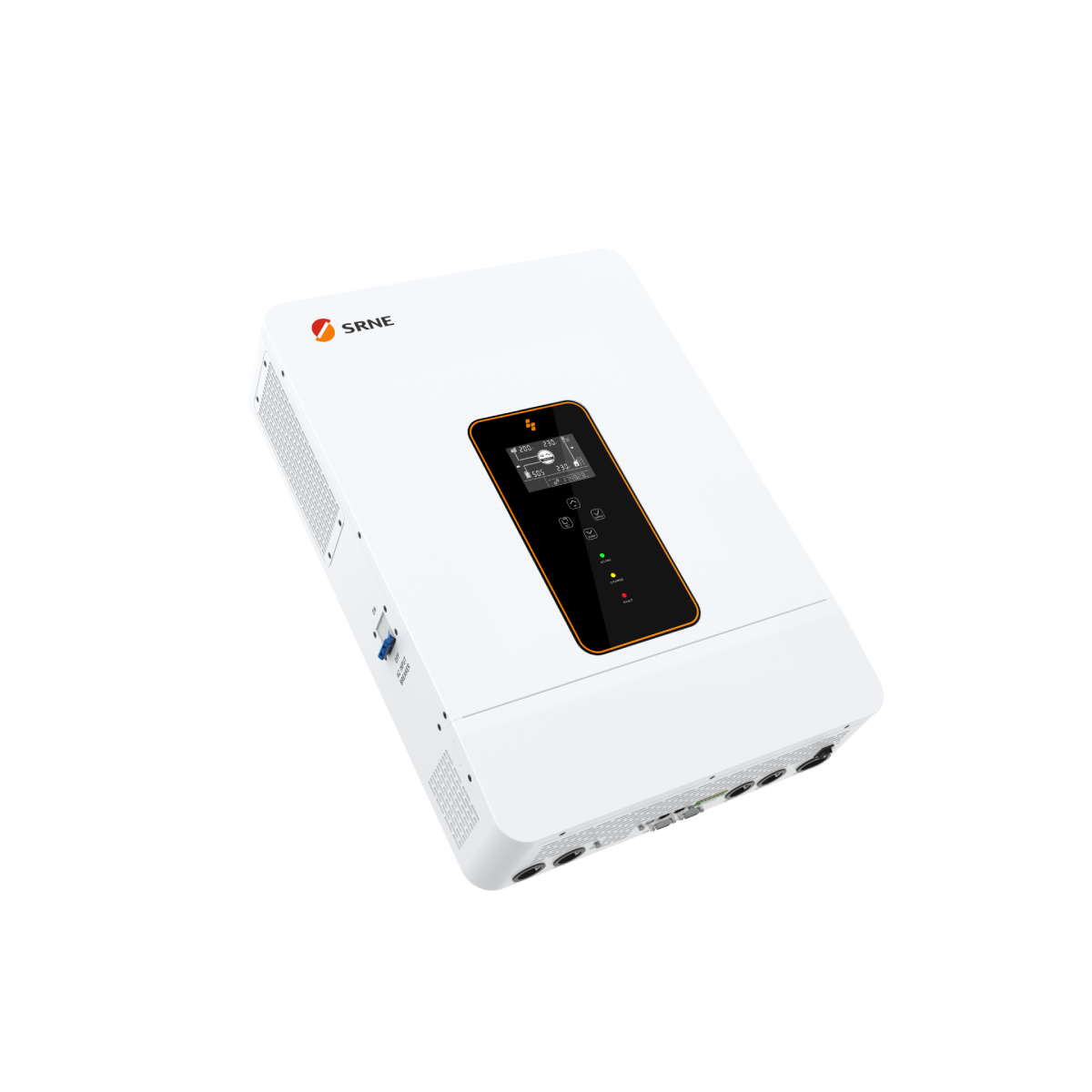
In fact, SRNE Off-Grid Solar Inverter ASF/ASP Series suitable for use in remote areas,easy to install and simple to use.It's perfect for In locations where the utility grid is unavailable or unreliable.
The superiority of solar inverters is best illustrated through real-world deployments:
East Africa – Rural Solar Hub: In a remote village in East Africa, a solar microgrid powers a community school and health post. The system utilizes a standalone off-grid inverter to deliver uninterrupted electricity from solar panels and batteries, bypassing an unreliable or nonexistent utility infrastructure.
Western China – Highland Nomadic Camps: Among the mountainous regions of Northwestern China, nomadic herders rely on 5kW off-grid inverters combined with lithium batteries. These systems support essential services—lighting, satellite communication, and refrigeration—even during long, sun-scarce winters where grid access is impossible.
Australia – Remote Agricultural Farm: On a self-sufficient farm in rural Australia, a 10kW off-grid inverter powers irrigation systems, refrigeration units, and workshop equipment. Integrated with solar and battery storage, it significantly cuts down diesel generator use while ensuring stable daily operations.
These scenarios reflect the core advantage of off-grid solar inverters: they are engineered for environments where power autonomy is non-negotiable. Whether it's a humanitarian application, off-grid homestead, or industrial use in remote terrain, the off-grid solar inverter stands out as the most practical and reliable solution for maintaining power without the grid.
4.When Hybrid Inverters Make Sense—Even in Mostly Off-Grid Systems
While off-grid solar inverters are commonly favored for completely independent energy systems, there are specific scenarios where a MPPT hybrid inverter proves to be a more strategic choice—even in locations with minimal or no grid connection.
One such case involves temporarily disconnected properties, where access to the grid may become available in the near future. In these transitional environments, installing a MPPT hybrid inverter allows the system to operate in standalone mode today while remaining ready to integrate with utility power later—without requiring a complete system overhaul. This makes hybrid inverters a flexible solution for evolving infrastructure needs.
Another situation where hybrid inverters excel is in semi-autonomous households. These homes often function off-grid during the day using solar energy and batteries, but supplement power from the grid during nighttime or extended overcast periods. Hybrid inverters with MPPT functionality can seamlessly manage this dynamic, intelligently shifting between energy sources while simultaneously overseeing battery charging cycles and maintaining load stability.
A sustainable resort located on a remote Philippine island primarily operates without any public grid access. To reduce dependency on diesel generators and prepare for potential grid expansion, the resort adopted a hybrid inverter system paired with solar panels and lithium battery storage. Though the property functions off-grid most of the time, the inverter is configured to accept input from a backup generator and remains ready for future grid connectivity. This setup has resulted in considerable fuel savings and ensures long-term energy adaptability.
In such hybrid use cases, the inverter acts as a versatile control hub—balancing off-grid independence with the foresight to accommodate future energy options.
Learn more:
https://www.srnesolar.com/articledetail/the-role-of-home-power-inverters-in-off-grid-living.html
https://www.srnesolar.com/articledetail/is-off-grid-solar-inverter-worth-the-investment.html
Conclusion:
When it comes to creating a solar system that operates reliably and independently, especially in locations far from the grid, off-grid inverters are often the better choice. They’re simple to install, dependable in operation, and purpose-built for full autonomy. While hybrid inverters provide more flexibility in grid-connected environments or evolving infrastructures, their reliance on grid presence can be a limitation in fully off-grid scenarios.