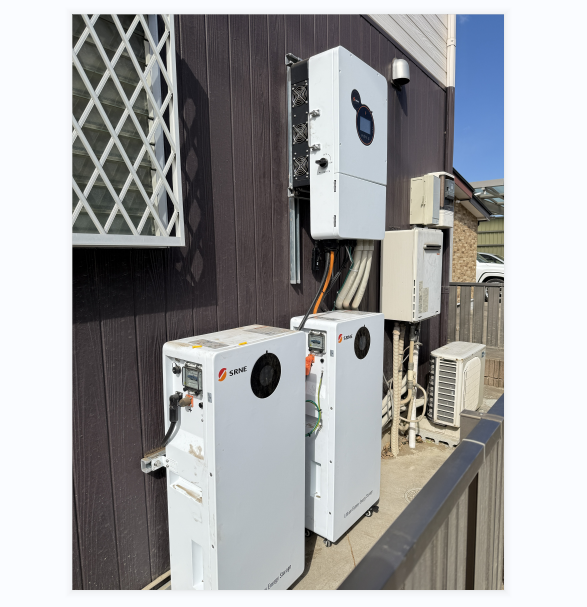
How to Select a Solar Storage Battery
Solar storage battery is the storage battery which is applied to solar power system. The solar battery extends the use of a PV system’s generated energy and will provide free, sustainable power even when there is not enough sunlight and the panels don’t produce energy. Therefore, selecting a suitable solar storage battery is possibly the biggest decision to be made if planning a solar power system of any size.
There are certain specifications you should use when evaluating your solar battery options, such as how long the solar battery will last or how much power it can provide. Below, learn about all of the criteria that you are supposed to use to compare the different types of solar batteries.
Storage Capacity
Capacity is the total amount of electricity that a solar battery can store, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Most home solar batteries are designed to be “stackable”, which means that you can include multiple batteries with your solar-plus-storage system to get extra capacity.
The size or capacity of the storage system should be appropriate to meet residential consumption demand. In principle, the storage system should be large enough to supply a household with solar power all the night. A battery capacity of 4 to 8 kWh is usually sufficient for an average four-person home consuming around 4,500 kWh annually. A poorly calculated battery system usually results in unnecessary extra costs. If the storage system is too small, not enough energy can be stored to cover the needs. The purchase of additional power from the grid becomes necessary. If the storage system is too large on the other hand, unneeded power is permanently stored, reducing the battery’s service life and not saving you any cost.
Power
While capacity tells you how big your battery is, it doesn’t tell you how much electricity a battery can provide at a given moment. To get the deeper understanding of the battery, you also need to consider the battery’s power rating. In the context of solar batteries, a power rating is the amount of electricity that a battery can deliver at one time. It is measured in kilowatts (kW).
With a high capacity and a low power rating, a solar battery would deliver a small amount of electricity (enough to run a few crucial appliances) for a long time. A battery with low capacity and a high power rating could run your entire home, but only for a few hours.
Depth of Discharge (DoD)
Expressed as a percentage, the depth of discharge (DoD) is the amount of energy that can be safely used without accelerating battery degradation. Most manufacturers will specify a maximum DoD for optimal performance. For example, if a 10 kWh battery has a DoD of 90 percent, you shouldn’t use more than 9 kWh of the battery before recharging it. Generally speaking, a higher DoD means you will be able to utilize more of your battery’s capacity.
As for the different types of storage battery, lithium batteries can be safely discharged to about 80-90% of their nominal capacity. Lead-acid batteries can typically by discharged to about 50-60%, while flow batteries can be discharged 100%.
Battery Efficiency
A solar battery’s round-trip efficiency represents the amount of energy that can be used as a percentage of the amount of energy that it took to store it. For example, if you feed 5 kWh of electricity into your battery and can only get 4 kWh of useful electricity back, the battery has 80 percent round-trip efficiency (4 kWh / 5 kWh = 80%). Generally speaking, a higher round-trip efficiency means you will get more economic value out of your battery. However, there is always some conversion loss, but a lithium battery usually be more than 90% efficient.
Battery Lifespan
The expected life of the battery (and its warranty) can be rated in cycles or years (which is generally an estimate based on the expected typical usage of the battery). The lifespan should also state the expected level of capacity at the end of life.
For example, a battery might be warrantied for 5,000 cycles or 10 years at 70 percent of its original capacity. This means that at the end of the warranty, the battery will have lost no more than 30 percent of its original ability to store energy. For lithium batteries this will usually be about 60–80% of the original capacity.
Conclusion
Advanced technology, a long service life, and recently reduced prices make PV storage systems a worthwhile investment. With a suitable battery storage system, you can use the solar power from your system when you really need it and permanently lower your electricity bills.