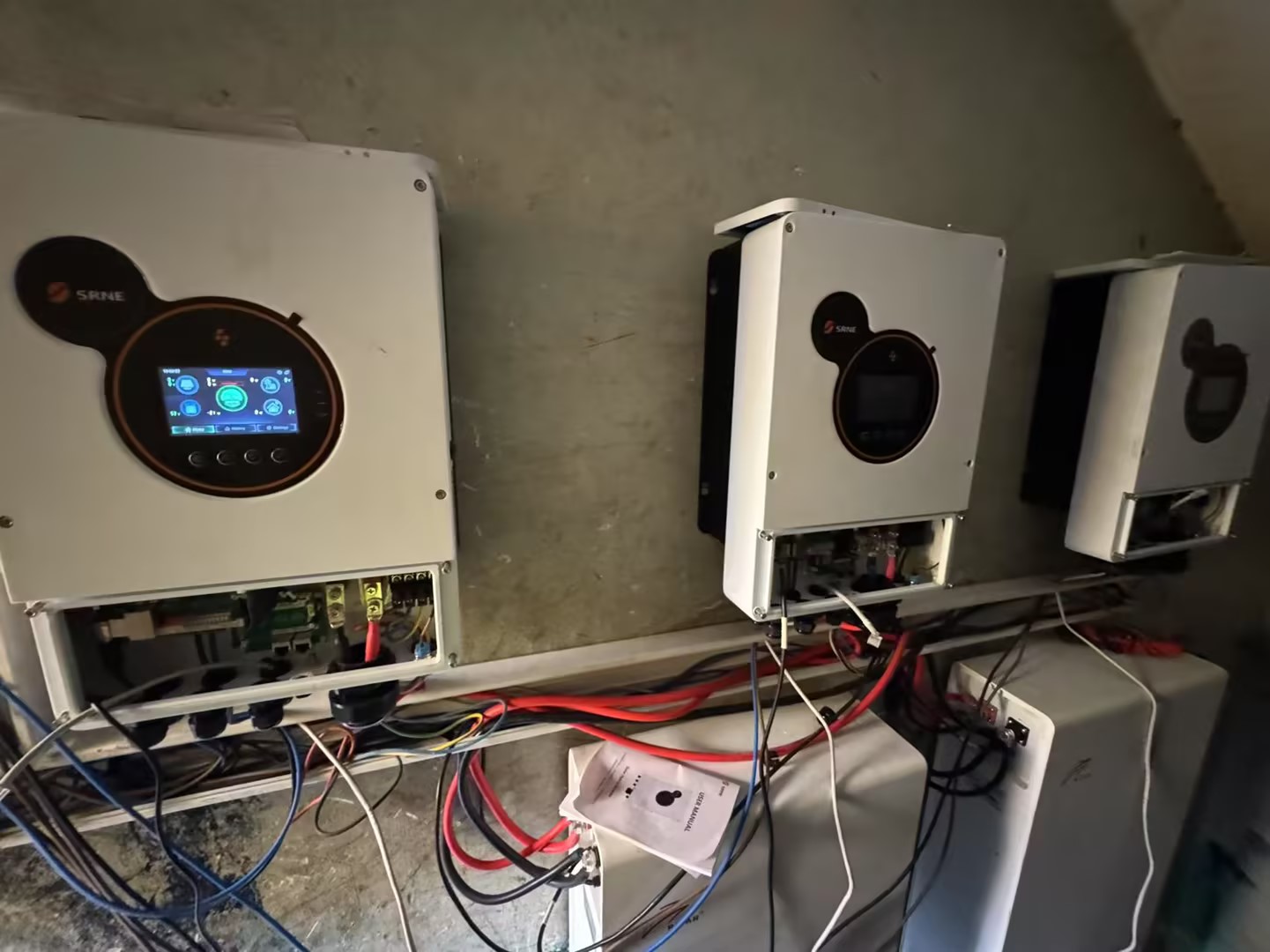
How much do you know about solar energy storage
The generation of energy required to meet the increasing global demand should not compromise the environment and the future of the planet. Nowadays renewable energies have been identified as potential alternatives to fossil fuels which do harm to the plant with CO2 emissions. Subsequently, solar energy is seen as the most versatile and the largest source of heat and electricity for the future globally.
However, as solar is an intermittent source and has variable outputs, energy storage technologies are required in order to facilitate the heat and electricity demands from solar energy and to ensure that the supply matches these demand. Most importantly, the high-efficiency utilization of solar energy necessitates considerable advancement in energy storage technologies and materials to overcome its intermittent nature.

What is energy storage?
“Storage” refers to technologies that can capture electricity, store it as another form of energy (chemical, thermal,mechanical), and then release it for use when it is needed. Although using energy storage is never 100% efficient—some energy is always lost in converting energy and retrieving it—storage allows the flexible use of energy at different times from when it was generated. So, storage can increase system efficiency and resilience, and it can improve power quality by matching supply and demand.
Capacity is the total amount of electricity that a storage system can store, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Different energy and power capacities of storage can be used to manage different tasks. Short-term storage that lasts just a few minutes will ensure a solar plant operates smoothly during output fluctuations due to passing clouds, while longer-term storage can help provide supply over days or weeks when solar energy production is low or during a major weather event, for example.
The benefits of storing solar energy
Balancing electricity loads
Without storage, electricity must be generated and consumed at the same time, which may mean that grid operators take some generation offline, or “curtail” it, to avoid over-generation and grid reliability issues. Conversely, there may be other times, after sunset or on cloudy days, when there is little solar production but plenty of demand for power. Enter storage, which can be filled or charged when generation is high and power consumption is low, then dispensed when the load or demand is high. When some of the electricity produced by the sun is put into storage, that electricity can be used whenever grid operators need it, including after the sun has set. In this way, storage acts as an insurance policy for sunshine.
Providing resilience
Solar energy storage can provide backup power during an electrical disruption. They can keep critical facilities normally operating to ensure continuous essential services, like communications. Solar energy storage can also be used for microgrids and smaller-scale applications, like mobile or portable power units.
Firming solar generation
Short-term storage can ensure that quick changes in generation don’t greatly affect the output of a solar power system. For example, a small battery can be used to ride through a brief generation disruption from a passing cloud, helping the grid maintain a “firm” electrical supply that is reliable and consistent.
The Common Solar Energy Storage Type
There’s no silver bullet solution for solar energy storage. Solar energy storage solutions depend on your requirements and available resources.
Commercial Solar Energy Storage
There are two key benefits that energy storage provides. First and foremost, most homes and businesses install storage for the resiliency benefit: backup power in the event of a grid outage. But for many commercial applications, energy storage can provide much greater financial benefits than it can to homeowners, especially if your business is on a complex utility rate with either demand charges or a time-varying price for electricity.
Home Solar Energy Storage
Residential solar has myriad benefits, including resiliency, cost savings, and decentralization of electrical production (otherwise known as “virtual power plants”). But the commercial energy storage methods we discussed above are likely cost-prohibitive for the average homeowner. Thankfully, battery storage can now offer homeowners a cost-effective and efficient way to store solar energy.
The sun offers a limitless supply of clean power, but harnessing it can be a challenge. Thankfully, several options for commercial and residential storage offer proven solutions for storing solar energy. The energy storage technologies are being developed daily. The future for energy storage is bright.