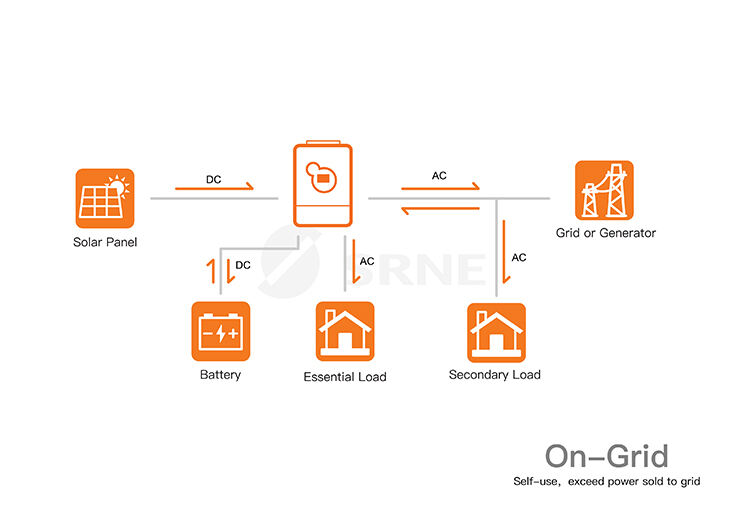
What Are the Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid?
What Are the Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar?
On-grid and off-grid solar systems are two main types of solar power setups, each with distinct characteristics and purposes. Here are the key differences between them:
1. Connection to the Grid:
- On-Grid (Grid-Tied) Solar System: An on-grid solar system is connected to the local electrical grid. It generates electricity from the sun using solar panels, and any excess energy not immediately used by the home or business is sent back to the grid. This excess energy is often credited or compensated for through net metering or feed-in tariffs, reducing the owner's electricity bill.
- Off-Grid Solar System:An off-grid solar system operates independently of the electrical grid. It generates electricity that is used directly by the home or business and stored in batteries for use when the sun is not shining. Off-grid systems are common in remote or rural areas where grid access is unavailable or expensive to establish.
2. Energy Independence:
- On-Grid:On-grid systems still rely on the grid for power supply during times when the solar panels are not producing energy (e.g., at night or during cloudy days). They don't provide energy independence in the event of grid outages.
- Off-Grid: Off-grid systems provide energy independence, as they are entirely self-sustained and do not rely on the grid. They are designed to meet the energy needs of the property without external power sources.
3. Battery Storage:
- On-Grid: On-grid systems may or may not include battery storage. If they do, batteries are often used to store excess energy for later use during peak demand periods, but they might not be sufficient to provide power during prolonged outages.
- Off-Grid: Off-grid systems almost always include battery storage to store surplus energy generated during sunny periods. These batteries ensure a consistent power supply during nighttime or cloudy days.
4. Cost Considerations:
- On-Grid: On-grid systems tend to be less expensive initially since they do not require as many batteries or complex off-grid equipment. The return on investment comes mainly from reduced energy bills and potential incentives.
- Off-Grid: Off-grid systems are typically more expensive due to the added cost of battery storage and backup power systems. These costs are often offset by the savings of not having to extend utility lines to remote locations.
5. Maintenance and Complexity:
- On-Grid: On-grid systems are simpler and often require less maintenance because they do not need to manage battery systems. Maintenance mainly involves checking and cleaning solar panels.
- Off-Grid: Off-grid systems are more complex and require more maintenance due to the presence of battery banks. Batteries need regular maintenance and replacement to ensure the system's longevity.
6. Environmental Considerations:
- Both on-grid and off-grid systems contribute to reducing carbon emissions by generating clean, renewable energy. However, off-grid systems can have a more significant environmental impact in remote areas by replacing diesel generators, which are often used as the primary power source.
Ultimately, the choice between on-grid and off-grid solar depends on factors such as the availability of grid access, energy independence goals, budget, location, and specific energy needs.
SRNE Inverters have different power for you to choose,and our storage battery can be combined with SRNE brand inverter to form an off-grid photovoltaic system, which can solve the problem of electricity consumption in areas without electricity.
Main features of off-grid inverters:
Off-grid inverters play a crucial role in off-grid solar systems by converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels and stored in batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power household appliances and electronics. Here are the main features of off-grid inverters:
1. Inverter Type: Off-grid inverters are specifically designed for use in systems that are not connected to the grid. They are different from grid-tied inverters, which synchronize with the utility grid.
2. Pure Sine Wave Output: High-quality off-grid inverters produce a pure sine wave AC output, which is the same type of electricity that comes from the grid. This clean output is compatible with all types of appliances and electronics, ensuring they run efficiently and without damage.
3. Output Power Capacity: Off-grid inverters come in various power capacities, ranging from a few hundred watts to several kilowatts. The choice of inverter capacity depends on your energy consumption needs and the total load you plan to power.
4. Surge Capacity: Some off-grid inverters have surge capacity, allowing them to handle short-duration high-power demands, such as when starting up certain appliances or motors.
5. Input Voltage Range: Off-grid inverters are designed to work with the voltage range of the battery bank they're connected to. This voltage range might be 12V, 24V, 48V, or higher, depending on the battery configuration.
6. Battery Charging: Many off-grid inverters have built-in battery chargers that can recharge the battery bank using AC power sources, such as a generator or grid connection, when solar production is insufficient.
7. Battery Monitoring: Some inverters offer battery monitoring features that display the battery's state of charge, voltage, and other relevant information. This helps users manage their energy consumption and storage effectively.
8. Remote Monitoring: Advanced off-grid inverters might come with remote monitoring capabilities, allowing you to monitor the system's performance and status remotely through a computer or smartphone app.
9. Load Management: Certain inverters have load management features that prioritize specific loads when the available energy is limited. This can help avoid overloading the system during periods of low solar production.
10. Protection Mechanisms: Off-grid inverters often include protection mechanisms to safeguard against overloads, short circuits, overheating, and other potential issues that could damage the inverter or connected devices.
11. Expandability: Some off-grid inverters can be easily expanded by connecting multiple units together to increase power capacity as your energy needs grow.
12. Efficiency: The efficiency of an off-grid inverter refers to how effectively it converts DC power into AC power. High-efficiency inverters reduce energy losses and maximize the utilization of available solar energy.
13. Warranty: Reputable manufacturers offer warranties for their off-grid inverters, providing peace of mind and support in case of malfunctions or defects.
Main features of on-grid inverters:
On-grid inverters, also known as grid-tied inverters, are a crucial component of solar energy systems that are connected to the electrical grid. They convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be fed into the grid or used by the property. Here are the main features of on-grid inverters:
1. Grid Synchronization: On-grid inverters synchronize with the frequency and voltage of the utility grid to ensure that the electricity they produce is in phase with the grid's electricity. This synchronization allows for seamless integration of solar power into the grid.
2. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT): Many on-grid inverters include MPPT technology, which optimizes the solar panel system's performance by ensuring that the panels operate at their maximum power output under varying sunlight conditions.
3. High Efficiency: On-grid inverters are designed to efficiently convert DC electricity from solar panels into AC electricity for use in the property or to be fed into the grid. High efficiency helps maximize the energy production of the solar system.
4. Power Capacity: On-grid inverters come in various power capacities, ranging from small residential systems to large commercial installations. The choice of inverter capacity depends on the size of the solar array and the expected energy production.
5. Voltage Range: On-grid inverters are designed to operate within specific voltage ranges based on the grid's voltage specifications. They need to ensure that the electricity they generate aligns with the grid's voltage.
6. Monitoring and Data Logging: Many on-grid inverters offer monitoring and data logging features. This allows users to track the system's performance, energy production, and other key metrics in real time. Some inverters also come with online platforms or apps for remote monitoring.
7. Safety Features: On-grid inverters incorporate safety mechanisms to protect against voltage surges, short circuits, overloads, and other electrical anomalies. These features help safeguard the inverter and the grid.
8. Anti-Islanding Protection: Anti-islanding protection is a critical safety feature that prevents the solar system from continuing to feed electricity into the grid during a power outage. This protects utility workers who might be working on the grid.
9. Remote Shutdown: Some on-grid inverters have remote shutdown capabilities, which allow utility companies or system owners to remotely shut down the solar system for maintenance or safety reasons.
10. Warranty: Reputable manufacturers offer warranties for their on-grid inverters, providing coverage for a specified period against defects or malfunctions.
11. String or Microinverter Options: On-grid systems can use string inverters, which handle the output of multiple solar panels connected in series, or microinverters, which are installed on individual panels and allow for panel-level optimization.
12. Rapid Shutdown: In some regions, rapid shutdown functionality is required by regulations. This feature ensures that the solar system can be quickly de-energized in case of emergencies or maintenance.
When selecting an inverter, it's important to consider factors such as the inverter's capacity, compatibility with your solar panels, monitoring capabilities, efficiency, and whether any local regulations or requirements need to be met. Consulting with solar professionals can help you choose the right on-grid inverter for your specific solar energy system.